 |
|
GNSS Antenna Phase Centre Calibration |
|
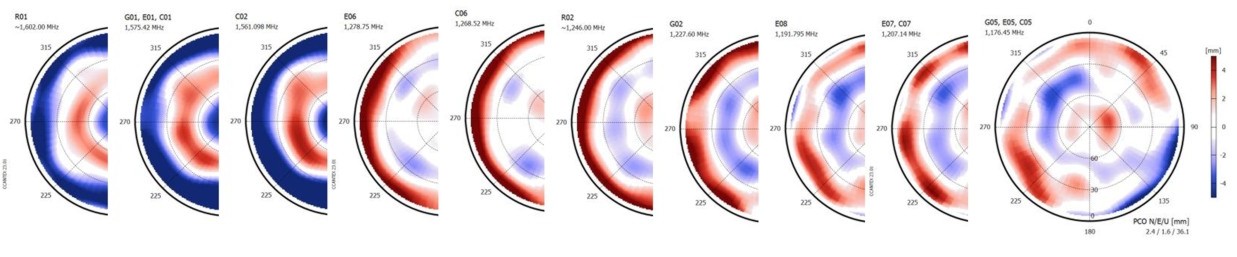
The effective electrical phase centre of a GNSS antenna does not coincide exactly with its mechanical centre. Furthermore, the electrical phase centre is not a physical point but changes with azimuth and elevation of the incident signal. It is frequency dependent and may vary significantly with any structural changes of the antenna (e.g. adding or removing a ground plane, choke rings or a radome). The differences to the mechanical phase centre can reach values in the range of 1 millimetre and 1 centimetre for most geodetic antennas. Its effect on positioning results can be larger by one order of magnitude. Phase centre offsets (PCO) and phase centre variations (PCV) with respect to an antenna reference point (ARP) are determined by GNSS antenna calibration. Both types of correction values are interdependent, i.e. they must always be applied together. PCO and PCV differences even occur for antennas of the same type. This may be caused by variations in the production process or by production errors like e.g. the incorrect fastening of the antenna element on its mount. Therefore, every geodetic GNSS antenna must be calibrated prior to its first use. An initial calibration is usually sufficient as temporal variations of PCO and PCV have rarely been reported. Wa2Ant serves for data processing of GNSS antenna calibrations performed relative to a reference antenna. Reference antenna and test antenna need to be employed on pillars of a local array. Observations are recorded for several azimuthal orientations of the antenna to be calibrated. An observation time of 12 to 24 hours is needed when using a device which allows measurements in several orientations per minute (e.g. DRB of Geodetic Institute at TU Dresden). If the antenna is rotated by hand, several 24 h sessions must be recorded. The data processing requires absolute phase centre corrections of the reference antenna. The calibration result consists of absolute corrections of the phase centre offset (PCO) and of the phase centre variations (PCV) for those GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou frequency bands being supported by the antenna, its receiver and the reference station. The following figure shows the DRB calibration results of a GNSS antenna at 10 frequencies: |
 |
| In recent years several hundred GNSS antenna calibrations have been processed using Wa2Ant or one of its predecessors Wa1/Kalib and WaSoft/Kalib. |
|
WaSoft.de, 2023 |